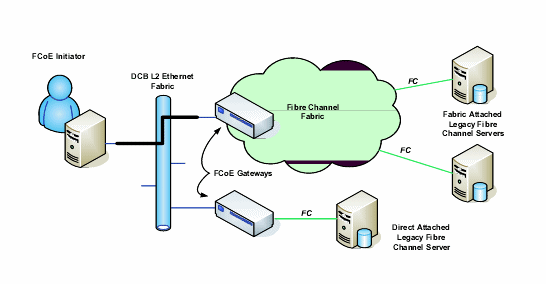
Intel® Ethernet FCoE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) is designed for the 82599 and X540-based 10 Gigabit family of PCI-Express server adapters. This guide covers hardware and software installation, setup procedures, known issues and troubleshooting tips for installing and booting the system using these adapters.
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is defined as the encapsulation of standard Fibre Channel (FC) protocol frames as data within standard Ethernet frames. This link-level encapsulation, teamed with an FCoE-aware Ethernet-to-FC gateway, acts to extend an FC fabric to include Ethernet-based host connectivity. The FCoE specification focuses on encapsulation of FC frames specific to storage class traffic, as defined by the Fibre Channel FC-4 FCP specification. FC is a market-leading technology used to create Storage Area Networks (SANs).
Data Center Bridging (DCB) is a collection of standards-based extensions to classical Ethernet. It provides a lossless data center transport layer that enables the convergence of LANs and SANs onto a single unified fabric. In addition to supporting Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and iSCSI over DCB, it enhances the operation of other business-critical traffic.

Key Terms
The following table defines key VN2VN terms:| N_Port | A device port that generates/terminates FC-4 channel traffic |
| ENode (FCoE Node) | A Fiber Channel node (FC-FS-3) that is able to transmit FCoE frames using one or more ENode MACs |
| FCoE_LEP (FCoE Link End-Point) | The data forwarding component of an FCoE Entity that handles FC frame encapsulation/decapsulation, and transmission/reception of encapsulated frames through a single Virtual Link |
| Lossless Ethernet network | An Ethernet network composed only of full duplex links, Lossless Ethernet MACs, and Lossless Ethernet bridging elements |
| Virtual Link | The logical link connecting two FCoE_LEPs |
| VN_Port (Virtual N_Port) | An instance of the FC-2V sublevel of Fibre Channel that operates as an N_Port (see FC-FS-3) and is dynamically instantiated on successful completion of a FIP FLOGI or FIP NPIV FDISC Exchange |
| VN_Port MAC address | The MAC address used by an ENode for a particular VN_Port |
What is VN to VN?
FCoE VN toVN support, also called VN2VN, is a new proposal standard by T11 for connecting two end-nodes (ENodes) directly using FCoE. An ENode can create a VN2VN virtual link with another remote ENode by not connecting to FC or FCoE switches (FCFs) in between, so neither port zoning nor advance fibre channel services is required. The storage software has to control the access and security of LUNs using LUN masking. The VN2VN fabric may have a lossless Ethernet switch between the ENodes. This will allow multiple ENodes to participate in creating more than one VN2VN virtual link in the VN2VN fabric. VN2VN has two operational modes: Point to Point S(PT2PT) and Multipoint.
| NOTE: The mode of operation is used only during initialization. |
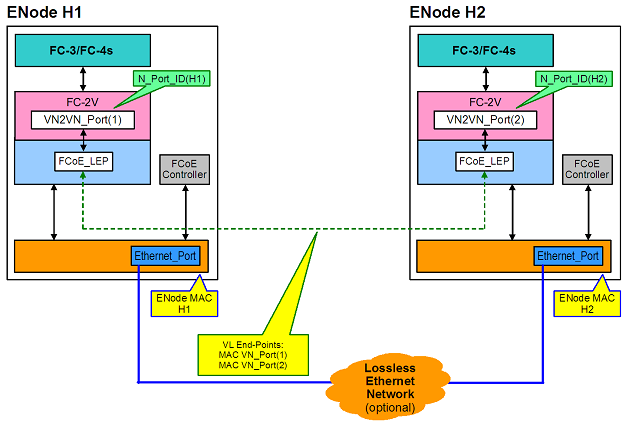
Point to Point (PT2PT) Mode
In Point to Point mode, there are only two ENodes, and they are connected either directly or thru a lossless Ethernet switch::
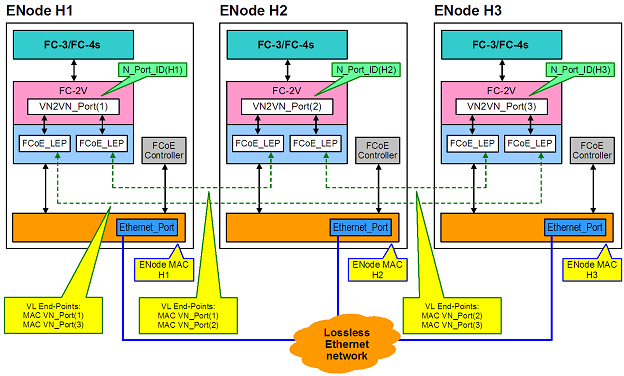
If more than two ENodes are detected in the VN2VN fabric, then all nodes should operate in Multipoint mode:
For information on system requirements see System Requirements.
The following is a typical FCoE setup flow:
Last modified on 8/24/11 10:28a Revision